Description of the National Plant Protection Organization (NPPO) of Germany
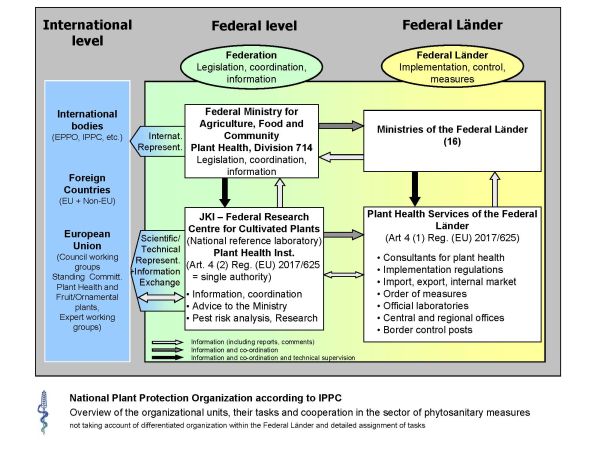
Figure: ![]() Organizational chart of the National Plant Protection Organisation Germany
Organizational chart of the National Plant Protection Organisation Germany
13/05/2025, PDF
Tasks and organization follow the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC, Art. IV) and the regulations of the European Union in the phytosanitary field.
Institutions
The National Plant Protection Organization in Germany is formed by the following institutions with different responsibilities:
- On federation level, responsibilities for plant protection and plant health under the Plant Protection Act lies with the
 Federal Ministry for Agriculture, Food and Community (BMLEH) which is responsible for relevant legislation and official representation of Germany on plant protection and plant health matters.
Federal Ministry for Agriculture, Food and Community (BMLEH) which is responsible for relevant legislation and official representation of Germany on plant protection and plant health matters. - The
 Julius Kühn-Institut (JKI), Federal Research Centre for Cultivated Plants, with its Institute for National and International Plant Health (Plant Health Institute) collaborates closely with the BMEL and provides technical and scientific advice to it. It is responsible for the information exchange, pest reporting and early warning, the coordination of phytosanitary measures on the technical level in Germany and the elaboration of the scientific/technical basis of phytosanitary measures, in particular pest risk analysis and related research.
Julius Kühn-Institut (JKI), Federal Research Centre for Cultivated Plants, with its Institute for National and International Plant Health (Plant Health Institute) collaborates closely with the BMEL and provides technical and scientific advice to it. It is responsible for the information exchange, pest reporting and early warning, the coordination of phytosanitary measures on the technical level in Germany and the elaboration of the scientific/technical basis of phytosanitary measures, in particular pest risk analysis and related research.The Plant Health Institute is involved in work with the European Commission, DG SANTE (Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), the European Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) and the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
- The official Plant Protection Services of the Federal Laender (federal states) are in charge of the execution of federal laws and orders and the application of the phytosanitary measures. They are in particular responsible for inspections of plants and plant products at import, export and transit and their movement as well as in production and trade within the EU. They are also responsible for surveillance in accordance with Article IV.2 (a-e, g, h) IPPC and they report to the JKI any occurrence of relevant harmful organisms. The plant protection services of the federal states are equipped with diagnostic laboratories for phytosanitary examinations. The official inspectors are officers and employees of the public administration. Legislative instructions and directives of the Federal Law and the Law of the Federal States are binding for their decisions. The issuance of Plant Health Certificates is only done by the official authority, the responsible Plant Protection Service of the Federal Laender.
The collaboration between the BMEL, the JKI, the Federal Laender and their official Plant Protection Services is shown in the organization chart above.
Enquiries on import and export of specific consignments should be addressed to the contacts of the responsible bodies of the Federal Laender > to or from which import or export is intended.
Enquiries regarding technical/scientific phytosanitary matters in general, pest reports from Germany and interceptions of specific consignments should be addressed to the JKI >.
The official contact point for IPPC issues in Germany is the ![]() Federal Ministry for Food and Agriculture.
Federal Ministry for Food and Agriculture.
Last update: 9th May, 2025